Application Rationalization
This UK government organization had outsourced application management, which had successfully enabled a reduction of overall run costs. However, as new applications were introduced, overlaps of application capabilities were clearly emerging.
The service management had been approached to drive simplification decisions but was not recognised to have sufficient experience and capacity. So the business approached us for independent advice to deliver a strategy and options for rationalization.
Key goals included:
- cost reduction
- productivity gains
- application modernization

Solutions proposed
Two main options were considered:
- Use best practice based on methods and tools specifically designed and optimised for application rationalisation focused efforts.
- Introduce best practice methodology and enterprise architecture tools
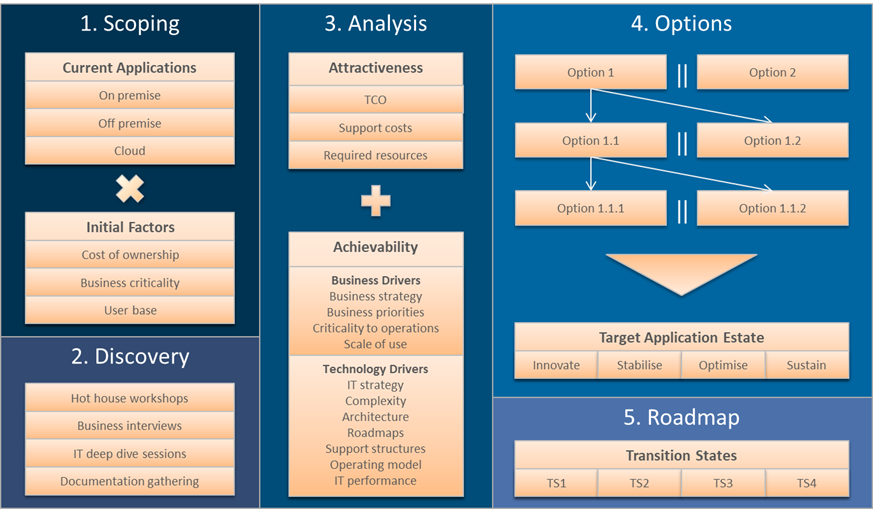
A tried and tested process that has proven successful in numerous previous engagements was selected. We worked closely with the client to tailor it to ensure that their specific focus areas and priorities were established. As illustrated in the following diagram, there were five stages to it.
Leveraging enterprise architecture tools is arguably ideally suited to enable evaluation of strategies for application rationalization, and consideration of multiple dependencies in the delivery roadmaps. One key benefit of EA tools, particularly where integrated with ITSM, is in program and portfolio management, supporting decision making with comprehensive and up to date business capability and application landscape viewpoints. It would also contribute to higher maturity of the client’s own architecture governance practice.
However, given the perceived risks identified in the RFI/RFP stage, due to current client practices and prerequisites, this was agreed as potential follow up activity.
Client contribution
During the RFP, the client provided an initial catalogue of the application portfolio in scope (comprising about 400 applications), namely information on active users, operational costs and the suppliers responsible for application management.
Examples of contributions during project delivery:
- Confirmation of established principles and standards by the enterprise architecture function, who approved the strategic direction
- A workspace, physical access and internet access to consultants as needed (on specific days, when the consultants needed to work out of client offices)
- Support for prioritisation of input documentation, stakeholder interviews and workshops so they were actioned expediently
- Assurance that Infrastructure costs were correlated to the application support and maintenance cost
A critical client contribution was to be able to discharge its obligations in a timely manner: for example, authorization of the project initiation, assignment of own resources, suppling information, accepting deliverables, etc
Outline
After a preliminary application of our scoping toolset to the list of applications provided, we proposed a staged approach. In this case, the stages were the following:
- Scoping, where we determined the applications to be subjected to the review.
- Discovery where we gathered information on application usage, Total Cost of Ownership, IT strategy, architecture and programmes and defined criteria and principles.
- Analysis, where we prioritised rationalisation activities for the in-scope applications. This led to the creation of the future state and roadmap.
- Options and constraints, where resource/programme constraints are considered and a hypothesis for rationalisation roadmap was created.
- This led to a roadmap development stage, transformation roadmap, the definition of an approach and architecture governance and to develop high level business case for rationalisation candidates

Preliminaries
Key aspects critical to the success of this application rationalization engagement included
- Appointment of a single point of contact for all requests for documentation and scheduling of stakeholder interviews and workshops.
- Agreement on project approach and stages.
- Confirmation of established principles and standards.
- Ensuring availability of service and business owners and other experts for interviews and hot house workshops.
Deliverables and outcomes
The deliverables initially identified evolved during the engagement, based on the client priorities. They included:
- Catalogue of in-scope applications
- Questionnaire template for application portfolio information gathering
- Engagement and interview / workshop plan
- Agreed evaluation criteria and weightings
- Information discovery repository
- Initial portfolio prioritisation
- Initial financial, functional and technical analysis
- Application duplication map
- Initial prioritisation for rationalisation opportunities
- Application portfolio rationalisation target state and outline roadmap
- Detailed roadmap definition report including benefits map
Requirements
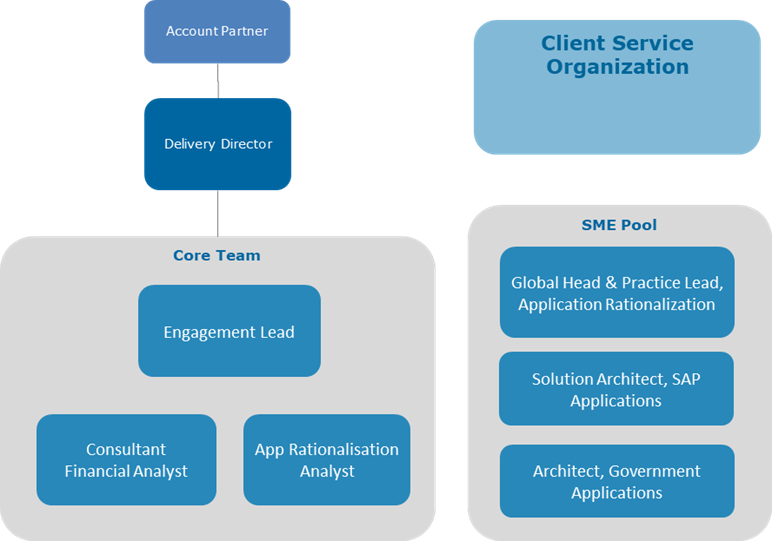
A core team of three was deployed in this project, supported by
- SME pool
- Delivery Director and Partner
- Client Service team
Enabled next steps
Beyond the expected application landscape transformation, which included various interventions like modernization, migration, consolidation, information archival, etc, several other initiatives were also enabled:
- Digital transformation
- Infrastructure refresh
- Business capability definition and assessment
- Disaster recovery planning
Notes
The client..
Feedback
The client..

